Sunday, 16 December 2012
Thursday, 13 December 2012
Profil Manusia
Profil mereka yang MEMPENGARUHI
Mereka bersifat peramah, bijak dalam pergaulan, ramai kawan dan ramai yang suka mendampingi mereka. Mereka ini petah berkomunikasi dan seorang yang bijak bersosial, suka menarik perhatian orang lain untuk terlibat bersama mereka.
Mereka ini cenderung untuk mengekalkan hubungan dengan mewujudkan suasana yang sentiasa
positif. Sifat penyayang dan keprihatinan yang ditunjukkan lebih menyifatkan
mereka ini mementingkan keharmornian.
Namun begitu kadangkala sikap terbuka mereka ini kadangkala memerangkap
diri mereka sendiri.
-RAH-
Monday, 10 December 2012
Lean in Supply Chain
Lean Supply Chain
contribution toward Lean Health Care
Edly Ferdin Ramly
Principal for EFR Management, Malaysia edly@efrmanagement.com
ABSTRACT
Lean systems allow a supply
chain to not only to be more efficient, but also faster. We can get our
sufficient supplies at right time, right quantity without any shortage or
excess inventory with effective lean supply chain. As the culture of lean takes
over the entire supply chain, all links increase their velocity. A culture of
rapid response and faster decisions becomes the expectation and the norm. However
leans supply chain always being left out during lean implementation in health
care.
Keywords: Lean Health care,
Just in time, Value Stream Map
INTRODUCTION
Lean thinking
are applicable anywhere there are processes to improve, including the entire
supply chain. A lean supply chain is one that produces just what and how much
is needed, when it is needed, and where it is needed.
The underlying
theme in lean thinking is to produce more or do more with fewer resources while
giving the end customer exactly what he or she wants. This means focusing on
each product and its value stream. To do this, organizations must be ready to
ask and understand which activities truly create value and which ones are
wasteful. The most important thing to remember is that lean is not simply about
eliminating waste—it is about eliminating waste and enhancing value.
The objectives
of this paper is to discuss the benefit and strategy ti implement lean supply
chain effectives. This synthesis based on single action base research enables
even small supplier or contractors to participate in the results of lean
efforts.
BENEFITS OF LEAN SUPPLY CHAIN
The main issues
in health care is increase of cost in medical supplies. The supplies included scientific
supply, medical supplies, linens, dietary, medical records, Patient
transportation and many more. All this supplies need to be
deliver in many areas in hospital including ward, clinics, laboratory and
theatres.Many supplies are everywhere and duplicate in many
location. Sometime excessive stock will lead to Out-of-date stock, less stock
will have erratic ordering, too many replenishment of supplies.
What benefit
the hospital when the hospital improve the supply chain? The hospital will able
to managed the supply chain effectively hence the expected results are:
•
Reduce purchasing cost
•
Reduce inventory
•
Reduce storage area
•
Improve warehouse control
•
Reduce lead time
•
Transportation cost
•
Reduce
error
A strong supply
chain enables the hospital to align themselves with each other and to
coordinate their continuous improvement efforts. Competitive advantage and
leadership in the global marketplace can only be gained by applying lean
principles to the supply chain. Thought, commitment, planning, collaboration,
and a path forward are required. A lean supply chain is proactive and plans for
the unexpected by positioning all resources for effectiveness. Downturns in
demand can be addressed without layoffs or significant productivity losses. What benefits the
organization as a whole benefits the supply chain.
LEAN SUPPLY CHAIN
STRATEGY
Supply chains
that want to grow and continue to improve must adopt lean. Lean concepts
require an attitude of continuous improvement with a bias for action. The
concepts of lean apply to all elements of the supply chain, including support
departments such as product development, quality, human resources, marketing,
finance, purchasing, and distribution. The challenge is to bring all of these
areas out of their traditional silos and make them work together to reduce
waste and create flow. Duplication and a lack of appropriate and timely
communication run rampant in these traditional organizations. All chain
partners have to be on the same playing field, and the lean concept is intended
to let everyone reach new levels of efficiency and effectiveness. Supply chain
leaders should not delay—it's urgent to act now to implement lean concepts in
the supply chain.
The strategy
relies on VIC strategy. The first strategy is to develop the value stream
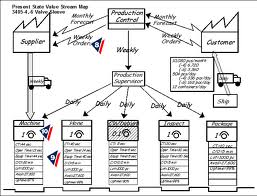
mapping (V). The value stream map (VSM) able to identify the process, the
supplier. However the supply chain detail, is not identify in first level and
second level of VSM. Additional information need to be integrate (I) to the
VSM. The detail may included the type of supply required for each process,
quantity required, pull or push system, and supermarket. The final strategy is to
control the supplies.

Figure 1: Material flow symbol (Rother and
Shook, 1999)
CASE STUDY
The
team from Hospital A are eager to implement lean. Almost all the service have been analyses using value
stream map. The first strategy has been completed. However the format of value
stream map, have the problem on identify the supplier. The solution is use the
VSM proposed by Nash and Poling (2008). The supplier sysmbol have eliminate and
start with the “patient”

Figure 2: The example of VSM for
diagnostic imaging
The second strategy was to integrate the
the supply chain information VSM. Most of common VSM don’t have space to
identify the supplies required for the process. There are suggestion to use
simple process mapping but the ideas not able to see the connection of the
supplies to the process and other department. The team decided to used the
bottom of process to list out the supplies for each process. Example during
preparation of patients, all the items are listed and quantity required is
quantified and at the same time the number stock kept and the way of the stock
replenished is added.
The last strategy is to identify the way
to control the stock. The pull with Kanban system and visual management is
always the best solution. But there were some cases where the supplies can be
eliminate at all for example film type of diagnostic change with electronic
imaging. 5S control was implemented and minimum stock especially for consumable
supplies i.e. paper table, drape exam sheet, glove, gauze; medical supplies
i.e. Kenalog, prep pad alcohol etc.
CONCLUSIONS
With VIC (VSM – Integrate - Control) strategy, the lean supply chains have
implemented effectively on the internal stock control. The value stream mapping
provide more visual diagram of the supplies flow in health care process. Since
in health care main focus is patient, and to provide more value to patient,
sometime the stock control not been capture in VSM. The additional integration
was used to capture the supplies and stock current and futire practices. The
next challenge of the hospital is extend the implementation to purchasing,
central store and lean supplier for example on just in time, reduction of batch
size (minimum order quantity) and pull system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank EFR
Management, Malaysia Productivity Corporation, National Iranian Productivity
Organization, Asia Productivity Organization, and management and staff of
Hospital A, Hasheminijad Kidney Centre, Tehran, Moheb Hospital, Tehran that provide the financial and resources
support in this research.
REFERENCES
Rother M and Shock J (1999),
“Learning to See”, Lean Enterprise
Institute
Arter D.R. (2008). Mapping
the total value stream mapping”, Productivity Press
Presented in
International Conference on Continuous Value Adding based on Lean Thinking in Hospital Management, Tehran, Iran,
30 Nov – 1 Dec 2011
Friday, 7 December 2012
LEAN - Step 3 Eliminate Waste
Strategi Penghapusan PEMBAZIRAN - Langkah 3 - Menghapuskan pembaziran
Selepas mengenalpasti pembaziran, seperti mana-mana proses penambahbaikan kita perlu mengenalpasti PUNCA mengapa pembaziran itu BERLAKU
Punca yang berkaitan secara langsung adalah kerana TAKUT-TAKUT
Punca yang contribute termasuklah:
Masalah Kualiti
Pekerja tidak mahir
Mencari barang, part, bahan mentah dsbg
Permintaan yang tidak menentu
Set-up mesin/ proses terlalu lama
Kerosakan sistem
Suka pada batch yang besar
Supplier lambat hantar
Kapasiti mesin, tempat dan ruang yang besar
Sebelum kita berbincang tentang beberapa alat (tools) dan teknik yang boleh digunakan, kita tengok apakah HIERARCHY Teknik-teknik penghapusan.
PERTAMA - HAPUSKAN TERUS apa-apa pembaziran yang tidak perlu atau yang boleh di ELAKKAN.
Contohnya, perlu ke kita cetak borang sedangkan sudah ada proses ONLINE
KEDUA - KURANGKAN
Contohnya, perlu ke kita menjalankan proses pengesahan sehingga 3 kali. Mungkin kita boleh hapuskan 2 proses tersebut dan tinggalkan 1
KETIGA - KOMBINEKAN
Kemungkinan kita boleh menggunakan alat (tools yang sesuai) seperti:
Masalah Kualiti - Poka Yoke, FMEA, Jidoka
Pekerja tidak mahir - Multiskill, empowerment etc
Mencari barang, part, bahan mentah dsbg - 5S
Permintaan yang tidak menentu - PULL, KANBAN sistem
Set-up mesin/ proses terlalu lama - SMED
Kerosakan sistem - TPM
Suka pada batch yang besar - One piece flow, looping, relayout etc, Heijunka
Supplier lambat hantar - Pull, JIT, Kanban
Kapasiti mesin, tempat dan ruang yang besar - Kecikkan tempat tu
Kebanyakan alat-alat diatas boleh menabantu mengeliminasi atau mengurangkan PEMBAZIRAN
Selamat mencuba
-CER-
Selepas mengenalpasti pembaziran, seperti mana-mana proses penambahbaikan kita perlu mengenalpasti PUNCA mengapa pembaziran itu BERLAKU
Punca yang berkaitan secara langsung adalah kerana TAKUT-TAKUT
Punca yang contribute termasuklah:
Masalah Kualiti
Pekerja tidak mahir
Mencari barang, part, bahan mentah dsbg
Permintaan yang tidak menentu
Set-up mesin/ proses terlalu lama
Kerosakan sistem
Suka pada batch yang besar
Supplier lambat hantar
Kapasiti mesin, tempat dan ruang yang besar
Sebelum kita berbincang tentang beberapa alat (tools) dan teknik yang boleh digunakan, kita tengok apakah HIERARCHY Teknik-teknik penghapusan.
PERTAMA - HAPUSKAN TERUS apa-apa pembaziran yang tidak perlu atau yang boleh di ELAKKAN.
Contohnya, perlu ke kita cetak borang sedangkan sudah ada proses ONLINE
KEDUA - KURANGKAN
Contohnya, perlu ke kita menjalankan proses pengesahan sehingga 3 kali. Mungkin kita boleh hapuskan 2 proses tersebut dan tinggalkan 1
KETIGA - KOMBINEKAN
Kemungkinan kita boleh menggunakan alat (tools yang sesuai) seperti:
Masalah Kualiti - Poka Yoke, FMEA, Jidoka
Pekerja tidak mahir - Multiskill, empowerment etc
Mencari barang, part, bahan mentah dsbg - 5S
Permintaan yang tidak menentu - PULL, KANBAN sistem
Set-up mesin/ proses terlalu lama - SMED
Kerosakan sistem - TPM
Suka pada batch yang besar - One piece flow, looping, relayout etc, Heijunka
Supplier lambat hantar - Pull, JIT, Kanban
Kapasiti mesin, tempat dan ruang yang besar - Kecikkan tempat tu
Kebanyakan alat-alat diatas boleh menabantu mengeliminasi atau mengurangkan PEMBAZIRAN
Selamat mencuba
-CER-
Thursday, 6 December 2012
LEAN Leadership
Sustaining
and spreading the gains in lean Hospitals: Role of Leadership
Edly Ferdin Ramly
ABSTRACT
Whether you follow
Lean, Six Sigma, or an internal methodology, one of the biggest challenges of
process improvement is ensuring that process changes are adopted
consistently—and sustained— and spread by your organization. How can you
measure how well your process improvements have been adopted? And how can you
monitor activity to ensure process improvements are sustained while identifying
new best practices for continuous improvement. The success factors of lean lies
on lean leadership.
Keywords: Lean Health care, Lean
Leadership
INTRODUCTION
People often equate “Lean” with the tools that are
used to create efficiencies and standardize processes. However, implementing
tools represents at most 20 percent of the effort in Lean transformations. The
other 80 percent of the effort is expended on changing leaders’ practices and
behaviors, and ultimately their mindset. Senior management has an essential
role in establishing conditions that enable that 80 percent of the effort to
succeed. Their involvement includes establishing governance arrangements that
cross divisional boundaries, supporting a thorough, long-term vision of the
organization’s value-producing processes, and holding everyone accountable for meeting
Lean commitments. This is accomplished through regular, direct involvement.
When upper management sets the example, durable Lean success and an
increasingly Lean leadership mindset follow.
Most of the literature on Lean conversions has
focused on implementing the Lean tools (to create flow, establish pull, support just-in-time production, etc.) in
manufacturing (Womack and Jones 1996; Rother and Shook 1998). Some of the
literature has explored Lean tools in healthcare, office settings, or product development
processes (Graban 2008); Critiques of
the tools only focus note that even brilliant use of tools without changes in
culture rarely produces lasting change, or even lasting .There is a missing link in Lean. This missing link
is the set of leadership behaviors and structures that make up a Lean
management system.Lean management bridges a critical divide: the gap between
Lean tools and Lean thinking. Systematic Lean management separates Lean
initiatives that start well but falter from those that sustain initial gains
and deliver further improvement.
In
this paper, we examines the key reasons why process changes often fail to be
sustained in the long term. Explore DIET techniques on how you can track
whether your organization is
really sustaining and spread the lean thinking
and continuous improvement.
FAILURE OF LEAN
IMPLEMENTATION
The lean effort
is consider failed once the organization stop their effort in waste elimination
stop. Stop mean the gain not been sustain and the implementation not been
spread. The main reason of failure are due to:
1. Purpose – The purpose of lean initiative have not been
clearly defined. In many cases, the organization adopted the lean just because
it is “the best menu of the day”.
2.
Process – The
process of the lean implementation not been plan, do, check and action. Yet, my own observations say this is
precisely the thing that most companies can’t seem to do. Why? Surely one major
reason for this is the way we lead and;
3. People – Employees didn’t buy in the initiative.
THE ROLES OF THE LEAN
LEADER
For hospital-wide Lean initiative to succeed, leaders at three
organizational levels must play complementary roles. This overlap reinforces
continuity of support for new practices throughout the organization, e.g.,
disciplined adherence, attention to process performance at intersections, and
gemba walking (which takes managers to the front lines to look for improvement
opportunities). This continuity maintains the internal integrity of Lean tool
implementations and the Lean management system.
Senior leaders play a central role in Lean
management. Their contributions are essential in:
1. Developing and implementing structures and
processes that anticipate and respond to the difficulties of a Lean initiative
that crosses internal boundaries;
2. Increasing the odds that process improvements
survive the transition from project mode to ongoing process and Creating
conditions in which a sustainable Lean culture of continuous improvement can
develop.;
3. Establishing and maintaining new,
process-focused measures along side conventional measures of results;
4. Transforming commitments to change into actual
change, supporting and sustaining new behaviors and practices;
The leader’s job at Toyota get each person to take initiative to solve problems and improve
his or her job. The Leader’s job is to
develop his or her people
spirit of Lean Mentorship. “If the learner hasn’t learned, the teacher hasn’t
taught”
Figure 1: Example of leadership model at
Toyota
Leadership at Toyota change from managing numbers to managing the process.Leaders at Toyota, like leaders anywhere,
want to see measurable results. But they know that the financial result is a result
of a process. They also realize that the financial results reflect
the past performance of that process. Far better is to create a process
that can be managed right NOW.
Leadership at Toyota also change from Problem-hiding to Problem-solving. All actions at Toyota revolve around planning
and problemsolving. It is assumed that there will be problems, that everything
will not go according to plan. “No problem is problem.” For the system to work,
problems must be exposed and dealt with forthrightly. Hiding problems will
undermine the system. Leadership at
Toyota utilised P-D-C-A. Toyota would say this is essentially the
P-D-C-A management cycle they learned from Dr. Deming.
Chairman Cho of Toyota:
Three Keys to Lean Leadership
- Go See - “Sr. Mgmt. must spend time on the plant floor.
- Ask Why - “Use the “Why?” technique daily.
- Show Respect. “Respect your people.”
In the early days of lean
implementation, the leader should allowed to just try things, to make mistakes and
learn from them. That’s the spirit that required in lean. “Continuous
improvement comes from making mistakes and learning from them." “It is a
mistake to suppose that men succeed through success; they much oftener succeed through
failures. Precept, study, advice, and example could never have taught them so
well as failure has done.”
CONCLUSIONS
Lean leadership is the key toward lean success.
The leader need to define the clear purpose of lean and ensure the first
project is the successful by giving full support and resources. Focus on
measure should be established based on process and transformed the commitment
in term coaching, education and respects.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank EFR
Management, Malaysia Productivity Corporation, National Iranian Productivity
Organization, Asia Productivity Organization, and management and staff of
Hospital A, Hasheminijad Kidney Centre, Tehran, Moheb Hospital, Tehran that provide the financial and resources
support in this research.
REFERENCES
Rother M and Shock J (1999),
“Learning to See”, Lean Enterprise
Institute
Graban
(2008), “Lean Hospitals: Improving Quality, Patient Safety, and Employee
Satisfaction “, Productivity Press
Presented at - International Conference on Continuous Value Adding based
on Lean Thinking in Hospital Management, Tehran, Iran,
30 Nov – 1 Dec 2011
Edly Ramly ã2011 www.efrmanagement.com and www.efrcertification.com
Tuesday, 4 December 2012
LEAN - Step 2 Identify Waste
Strategi Penghapusan PEMBAZIRAN - Langkah 2 - Mengenalpasti pembaziran
Untuk mengenalpasti pembaziran, ada beberapa alat (tools) dan teknik yang boleh digunakan. Tanpa Tools dan teknik, proses penegnalpastian boleh dilakukan juga. Tetapi ia mungkin tidak berapa efektif dan sukar untuk mendapatkan gambaran tentang dimana pembaziran berlaku, kenapa ia berlaku dan "how severe is it"
Teknik yang terkenal adalah teknik "Value Stream Mapping" yang diperkenalkan oleh Mike dan Rother didalam buku bertajuk "Learning to See".
Tool 1
Value stream mapping menngunakan kombinasi:
1) Carta aliran proses
2) Aliran maklumat
3) Maklumat berkaitan
- Masa Proses
- Masa Menunggu
- Jumlah invetori sebelum dan selepas proses
- Yield (ataupun Complete and Accurate)
- Bilangan tenaga kerja
dan berbagai lagi
Tool 2 = Process Mapping
Proses mapping adalah teknik analisa yang lebih detail untuk MASA sesuatu proses dijalankan. Teknik ini selalunya digunakan apabila proses di dalam VSM menunjukkan masa yang panjang diperlukan untuk menyiapkan sesuatu.
Proses mapping akan memecahkan proses kepada proses-proses yang lebih kecil supaya setiap proses itu boleh dikenalpasti pembazirannya.
Tool 3 = Spaghetti Diagram
Antara tools yang disukai ramai adalah spaghetti diagram. Diagram ini digunakan untuk mengenalpasti waste of motion dan conveyance didalam satu-satu kawasan.
Ada beberapa lagi tools yang boleh digunakan. Tetapi yang penting adalah pembaziran dapat dikenalpasti, digambarkan dan mudah untuk dibentangkan.
Seterusnya pembaziran ini perlu di labelkan. Biasanya dilabelkan dengan bintang letupan. Langkah seterusnya ialah... HAPUSKAN pembaziran tersebut
-CER-
Untuk mengenalpasti pembaziran, ada beberapa alat (tools) dan teknik yang boleh digunakan. Tanpa Tools dan teknik, proses penegnalpastian boleh dilakukan juga. Tetapi ia mungkin tidak berapa efektif dan sukar untuk mendapatkan gambaran tentang dimana pembaziran berlaku, kenapa ia berlaku dan "how severe is it"
Teknik yang terkenal adalah teknik "Value Stream Mapping" yang diperkenalkan oleh Mike dan Rother didalam buku bertajuk "Learning to See".
Tool 1
Value stream mapping menngunakan kombinasi:
1) Carta aliran proses
2) Aliran maklumat
3) Maklumat berkaitan
- Masa Proses
- Masa Menunggu
- Jumlah invetori sebelum dan selepas proses
- Yield (ataupun Complete and Accurate)
- Bilangan tenaga kerja
dan berbagai lagi
Tool 2 = Process Mapping
Proses mapping adalah teknik analisa yang lebih detail untuk MASA sesuatu proses dijalankan. Teknik ini selalunya digunakan apabila proses di dalam VSM menunjukkan masa yang panjang diperlukan untuk menyiapkan sesuatu.
Proses mapping akan memecahkan proses kepada proses-proses yang lebih kecil supaya setiap proses itu boleh dikenalpasti pembazirannya.
Tool 3 = Spaghetti Diagram
Antara tools yang disukai ramai adalah spaghetti diagram. Diagram ini digunakan untuk mengenalpasti waste of motion dan conveyance didalam satu-satu kawasan.
Ada beberapa lagi tools yang boleh digunakan. Tetapi yang penting adalah pembaziran dapat dikenalpasti, digambarkan dan mudah untuk dibentangkan.
Seterusnya pembaziran ini perlu di labelkan. Biasanya dilabelkan dengan bintang letupan. Langkah seterusnya ialah... HAPUSKAN pembaziran tersebut
-CER-
LEAN - Case Study - Sistem Penyampaian 1
Buat masa ini, banyak initiatif yang cuba dijalankan oleh kerajaan untuk menjadikan operasi mereka leboih lean. Sebelum saya kongsi beberapa case study lain yang diutara semasa sessi kurus lean beberapa agensi kerajaan yang lain, rencana ini dipetik daripada:
http://pmr.penerangan.gov.my/index.php/component/content/article/79-mengenai-kerajaan/8577-sistem-penyampaian-kerajaan-.html
Kerajaan sentiasa mengambil perhatian dan berusaha untuk meningkatkan
sistem penyampaian perkhidmatan semua kementerian dan agensi sektor awam.
Pelbagai tindakan susulan telah dilaksanakan dengan memberi penekanan kepada
lima (5) aspek berikut, iaitu:
· pembangunan Sumber Manusia;
·
pemantapan sistem dan prosedur kerja;
·
pengemaskinian undang-undang dan akta;
·
penggunaan ICT dalam penyampaian perkhidmatan; dan
·
pelaksanaan transformasi organisasi secara menyeluruh.
Selain daripada usaha berterusan seperti yang tersebut, mulai tahun 2007, kerajaan telah mengambil inisiatif untuk menubuhkan Pasukan Petugas Khas Pemudahcara Perniagaan, yang dikenali secara ringkas sebagai PEMUDAH. |
PEMUDAH merupakan satu perkongsian
bistari (smart partnership) di antara kerajaan dan sektor swasta yang diwakili
oleh Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers (FMM). PEMUDAH telah berjaya
menghasilkan beberapa pembaharuan dan peningkatan kecekapan penyampaian dengan
memudahcarakan prosidur dan tempoh pengurusan..
Contoh 1 - Tempoh pengeluaran
passport dari beberapa minggu sehingga hanya dua (2) jam yang merupakan satu
rekod sedunia.
Contoh 2:
Secara khusus, mengenai pemantapan pengurusan kewangan, sukacita dimaklumkan bahawa, melalui Surat Pekeliling Perbendaharaan Bil. 7 Tahun 2006, semua agensi Kerajaan dikehendaki menguruskan pembayaran bil dan tuntutan tidak lewat dari 14 hari dari tarikh ianya diterima. Berdasarkan pemantauan rapi yang dilaksanakan, prestasi agensi-agensi Kerajaan dalam menguruskan pembayaran bil dan tuntutan telah bertambah baik. Bagi tempoh 1 hingga 31 Oktober 2009 misalnya, prestasi pengurusan bil bagi 24 Kementerian adalah seperti berikut:
* Pembayaran dalam tempoh 14 hari ialah 96.67% dengan melibatkan 446,147 bil, di mana 86.66% mencapai tahap pembayaran dalam tempoh 7 hari yang melibatkan 391,858 bil
Secara khusus, mengenai pemantapan pengurusan kewangan, sukacita dimaklumkan bahawa, melalui Surat Pekeliling Perbendaharaan Bil. 7 Tahun 2006, semua agensi Kerajaan dikehendaki menguruskan pembayaran bil dan tuntutan tidak lewat dari 14 hari dari tarikh ianya diterima. Berdasarkan pemantauan rapi yang dilaksanakan, prestasi agensi-agensi Kerajaan dalam menguruskan pembayaran bil dan tuntutan telah bertambah baik. Bagi tempoh 1 hingga 31 Oktober 2009 misalnya, prestasi pengurusan bil bagi 24 Kementerian adalah seperti berikut:
* Pembayaran dalam tempoh 14 hari ialah 96.67% dengan melibatkan 446,147 bil, di mana 86.66% mencapai tahap pembayaran dalam tempoh 7 hari yang melibatkan 391,858 bil
* Pembayaran lewat iaitu melebihi 14 hari ialah 1.33% yang
melibatkan 6,030 bil
Contoh 3:
Contoh 3:
Untuk meningkatkan lagi kecekapan dalam menguruskan surat-menyurat,
Kerajaan telah menetapkan dalam para 6.10 Pekeliling Perkhidmatan Bilangan 5
Tahun 2007 bahawa semua surat yang diterima hendaklah diambil tindakan segera.
Sekiranya surat itu memerlukan jawapan segera, ia hendaklah dibalas dalam masa
yang singkat. Sekiranya jawapan segera tidak dapat diberikan, penulis surat itu
hendaklah dimaklumkan melalui surat akuan terima yang menyatakan bahawa
tindakan sedang diambil dan jawapan yang lengkap akan disusuli dalam satu
jangka masa yang dinyatakan.
Contoh 4: Lesen Perniagaan
Sila rujuk Blog MPC
http://blog.mpc.gov.my/index.php/2011/07/12/meningkatkan-penyampaian-perkhidmatan-sektor-awam-melalui-pemodenan-lesen-perniagaan?blog=6
Kerajaan akan terus berusaha gigih, dengan menggunakan kaedah pengurusan dan teknologi yang bersesuaian untuk terus meningkatkan lagi mutu system penyampaian sektor awam supaya lebih responsive serta dapat memenuhi kehendak rakyat jelata. Dalam pada ini, kerajaan sentiasa mengalu-alukan dan menghargai maklumbalas dan teguran secara spesifik daripada orang awam, dan khasnya daripada wakil rakyat.
-CER-
Monday, 3 December 2012
LEAN - Step 1 Awareness
Strategi pertama untuk perlakasanaan LEAN adalah kesedaran tentang WASTE ataupun PEMBAZIRAN.
Ramai yang tidak sedar, pembaziran ada didepan mata. Banyak juga terfikir tentang pembaziran elektrik, penjimatan kos dan sebagainya.
Ada pembaziran yang sudah menjadi akar umbi, manakala ada juga yang baru nak bermula.
Kita perlu faham sebelum lain-lain pembaziran berlaku, ia berlaku kerana ada PROSES yang tidak perly DILAKUKAN.
PROSES TIDAK PERLU
1) Termasuklah proses yang tidak diperlukan oleh PELANGGAN. Dalam erti kata lain, pelanggan tak kisah, kita buat ataupun tak buat.
- MENUNGGU
- PERGERAKAN DALAM PEJABAT
- MENYEMAK BERULANG-ULANG mahupun approval atau birokrasi
2) Proses yang tidak diperlukan oleh ORGANISASI. Selalunya proses ini dicipta kerana perasaan TAKUT-TAKUT
Contohnya -
takut-takut salah... jadi kena la check banyak kali
takut-takut tak cukup... beli barang banyak
takut-takut pelanggan minta
takut-takut BOSS marah
taku-takut mesin rosak
takut-takut ambik masa ynag lama untuk set-up
dan macam-macam takut-takut
SEMUA PROSES INI TIDAK MENAMBAH NILAI dan kita perlu sedar yang proses ini adalah PEMBAZIRAN.
-CER-
Ramai yang tidak sedar, pembaziran ada didepan mata. Banyak juga terfikir tentang pembaziran elektrik, penjimatan kos dan sebagainya.
Ada pembaziran yang sudah menjadi akar umbi, manakala ada juga yang baru nak bermula.
Kita perlu faham sebelum lain-lain pembaziran berlaku, ia berlaku kerana ada PROSES yang tidak perly DILAKUKAN.
PROSES TIDAK PERLU
1) Termasuklah proses yang tidak diperlukan oleh PELANGGAN. Dalam erti kata lain, pelanggan tak kisah, kita buat ataupun tak buat.
- MENUNGGU
- PERGERAKAN DALAM PEJABAT
- MENYEMAK BERULANG-ULANG mahupun approval atau birokrasi
2) Proses yang tidak diperlukan oleh ORGANISASI. Selalunya proses ini dicipta kerana perasaan TAKUT-TAKUT
Contohnya -
takut-takut salah... jadi kena la check banyak kali
takut-takut tak cukup... beli barang banyak
takut-takut pelanggan minta
takut-takut BOSS marah
taku-takut mesin rosak
takut-takut ambik masa ynag lama untuk set-up
dan macam-macam takut-takut
SEMUA PROSES INI TIDAK MENAMBAH NILAI dan kita perlu sedar yang proses ini adalah PEMBAZIRAN.
-CER-
Sunday, 2 December 2012
Apa itu LEAN?
Perkataan “Lean” menjadi
terkenal apabila Womack dan Jone menerbitkan buku “Lean Thinking” pada tahun
1996. Perkataan Lean digunakan bukan
bermaksud ... sandar. Jika kita lihat kamus bahasa Inggeris, Lean juga
bermaksud KURUS. Kaitan kurus, adalah menjalankan aktiviti dengan secara SLIM dan tak berlemak.
Lean dalam konteks kualiti dan kos bermaksud “EFISYEN”.
Efisyen bermaksud menjalankan aktiviti dengan mengoptimakan sumber, termasuklah
masa, sumber manusia, tenaga dan juga kewangan. Dalam masa yang sama, memenuhi
kehendak pelanggan dan meningkatkan kepuasan pelanggan.
Apakah MATLAMAT utama LEAN
Matlamat utama lean ada MENGHAPUSKAN pembaziran. Sbelum
perkataan lean digunakan, teknik yang sama digunakan oleh Lean adalah TPS
ataupun Toyota Production System. TPS telah diamalkan oleh pihak Jepun semenjak
tahun 60 an kerana mereka kekurangan sumber, termasuklah tanah dan sumber asli.
Jadi mereka kena memikirkan bagaimana untuk mengoptimakan sumber-sumber yang
ada.
Apakah PEMBAZIRAN
(WASTE) yang ada didalam operasi
Teknik VAVE (value analysis dan value engineering)
memfokuskan rekabentuk dan pembangunan
(design dan development) untuk produk, manakala LEAN memfokuskan kepada
operasi.
Ada TIGA jenis pembaziran
proses yang mudah untuk di INGATI iaitu
WAIT (TUNGGU)
CHECK (SEMAK)
MOVE (GERAK)
Manakala TOYOTA pula memperkenalkan 7 jenis Pembaziran
iaitu, Wait, Over-produce, Motion, Rework, over-proses, inventory dan
conveyance (ataupun transpirt). Ada yang menambah pembaziran Maklumat
)Information) dan berbagai lagi.
Apakah STRATEGI Lean.
Jika mengikut Lean
Thinking” ada 5 strategi. Tetapi saya lebih suka meringkaskan strategi LEAN
kepada TIGA iaitu:
1 1) SEDAR wujudnya PEMBAZIRAN
2) KENALPASTI Pembaziran itu dimana
3) HAPUSKAN atau KURANGKAN pembaziran tersebut
Ada berbagai teknik dan alat (tools) yang boleh digunakan
sperti menggunakan VSM, Poka YOKE, 5S dan lain-lain lagi.
SUDAHKAN anda melaksanakan LEAN. Keran apembaziran itu
adalah AMALAN SYAITAN
Salam hormat dari saya
\
-CER-
Di Sedenak, (untuk berfikir
sejenaka) Kulai
Workshop LEAN di Suzhou - Tahun 2001 kot
He he he... terjumpa gambar lama. Dalam banyak-banyak worksyop LEAN, ni je gambar yang jumpa... macam kelakar pulak tengok gmbar muda-muda dulu...
Dulu buat worksyop, kena hand-on sekali..
Entah faham ke tak pakcik ni...
Tangga buluh tu... he he
InsyaAllah, saya kongsikan apa itu Lean dan bagaimana melaksanakan lean...
-CER-
Dulu buat worksyop, kena hand-on sekali..
Entah faham ke tak pakcik ni...
Tangga buluh tu... he he
InsyaAllah, saya kongsikan apa itu Lean dan bagaimana melaksanakan lean...
-CER-
MINGGU LEAN
Minggu ni, saya ingin berkongsi sedikit tentang LEAN. Lean adalah antara bidang kepakaran saya selepas audit sistem pengurusan.
Lean antara antara bidang kerjaya saya yang pertama setelah dilantik sebagai Pegawai Promosi Lean pada tahun 2000. Walaupun sebelum itu saya tidak pernah dengar tentang Lean, saya bertuah kerana diberi kepercayaan untuk mempromosikan Lean untuk TRW (sebelum ini dikenali sebagai LUCAS) bersama mentor saya Mr Tom Draper daripada TRW US dan juga sahabat darupada plant-plant TRW yang lain termasuklah En Halim Baharom daripada TRW Bkt Beruntung, Ji Hong daripada Suzhou dan ramai lagi sahabat-sahabat yang lain dari seluruh pelusuk dunia.
Syukor, pada tahun lepas, saya bersama MPC Wilayah Pantai Tinur dapat melancarkan program LEAN kepada PKNP (PErbadanan Kemajuan Negeri Pahang) dan kemudian bersama-sama dengar pakar-pakar Lean yang lain daripada Jepun untuk bersama-sama menjadi mentor dan speaker untuk Lean Seminar untuk PENGURUSAN HOSPITAL di Iran.
Tahun ini, saya dapat bersama-sama dengan pengarah dan pegawai-pegawai MPC (Malaysia Productiviti Corporation) untuk berkongsi dan membangun pakar serta modul berkaitan Lean.
Minggu ini pula dalah minggu yang istemewa kerana saya dapat bersama-saya dengan Pengarah dan kakitangan Pejabat Tanah dan Galian negeri Perak untuk Taklimat Lean pada perhimpunan PTG PErak kali ke-8. Selepas itu saya berkongsi pengalaman dengan kakitangan Pejabat SUK negeri Pulau Pinang di Dewan Seri Pinang untuk sessi kursus lean.
InsyaAllah, saya akan kongsikan jugak, idea perlaksanaan lean dalam penambahbaikan Sistem Penyampaian PErkhimatan Awam. Mula-mula saya kan kongsikan apakah itu Lean.
Selamat membaca.
-CER-
29 Nov 2012
Dewan Sri Pinang, Pulau Pinang
Lean antara antara bidang kerjaya saya yang pertama setelah dilantik sebagai Pegawai Promosi Lean pada tahun 2000. Walaupun sebelum itu saya tidak pernah dengar tentang Lean, saya bertuah kerana diberi kepercayaan untuk mempromosikan Lean untuk TRW (sebelum ini dikenali sebagai LUCAS) bersama mentor saya Mr Tom Draper daripada TRW US dan juga sahabat darupada plant-plant TRW yang lain termasuklah En Halim Baharom daripada TRW Bkt Beruntung, Ji Hong daripada Suzhou dan ramai lagi sahabat-sahabat yang lain dari seluruh pelusuk dunia.
Bersama pakar-pakar LEan daripada APO
Tahun ini, saya dapat bersama-sama dengan pengarah dan pegawai-pegawai MPC (Malaysia Productiviti Corporation) untuk berkongsi dan membangun pakar serta modul berkaitan Lean.
Minggu ini pula dalah minggu yang istemewa kerana saya dapat bersama-saya dengan Pengarah dan kakitangan Pejabat Tanah dan Galian negeri Perak untuk Taklimat Lean pada perhimpunan PTG PErak kali ke-8. Selepas itu saya berkongsi pengalaman dengan kakitangan Pejabat SUK negeri Pulau Pinang di Dewan Seri Pinang untuk sessi kursus lean.
InsyaAllah, saya akan kongsikan jugak, idea perlaksanaan lean dalam penambahbaikan Sistem Penyampaian PErkhimatan Awam. Mula-mula saya kan kongsikan apakah itu Lean.
Selamat membaca.
-CER-
29 Nov 2012
Dewan Sri Pinang, Pulau Pinang
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)